vaccine delivery system pdf
Results with rHsp60 plus Cholera T oxin liposome-encapsulated. Store the vaccine appropriately 2.
The system returns results faster when you use more specific search criteria.

. For Frozen vaccine contact Merck at 1-800-637-2579. For example during H1N1 once vaccines became widely available pharmacies played an important role in. Healthcare system and successful delivery of this vaccine will need to incorporate new types of sites and approaches for vaccine delivery.
The main advantage of needle-free vaccines is that there is minimal contamination of. Intradermal Delivery of Vaccines Executive summary The dermis and epidermis of the human skin are rich in antigen-presenting cells. The recent success of mRNA vaccines in SARS-CoV-2 clinical trials is in part due to the development of.
Needle-free or transdermal vaccines must be delivered with a specialized system which usually drives the vaccine into the skin with a burst of compressed air or gas. 62 Management of Vaccines and logistics at State District and PHC levels 75 63 Distribution of Vaccines and Logistics 77 64 Distribution of Vaccines from PHC 82 65 Guidelines on Open Vial Policy for using multi-dose vials 83 66 Outreach Session Level 87 67 Alternate Vaccine Delivery System AVDS 87. The environmental impact of energy materials and processes used in immunization systems is mini-mized.
One objective of the WRAC Fish Immunology Project was to test novel delivery systems for fish vaccines. 14 Target audience This guidance document is primarily directed at national authorities who are responsible for the management implementation and monitoring of COVID-19 vaccine introduction and delivery in their countries. At least six projects produce a DNA vaccine using the S protein gene against COVID-19 at various stages of the clinical trial to evaluate the safety.
20082025 July 1 2008 Version. Vaccines are needed to play a key role in addressing emerging and re-emerging pathogens Development and registration of commercial vaccines is long 10-15 years and costly 2B Vaccine technology has changed little in 200 years Innovative technologies have the potential to fundamentally change the delivery of vaccines for both. 1 Development of a novel vaccine delivery system based on Gantrez nanoparticles Sara Gómez1 Carlos Gamazo1 Beatriz San Roman1 Christine Vauthier2 Marta Ferrer3 Juan M.
Competent and motivated personnel are empowered to handle immunization supply chain. Recent trends in vaccine delivery systems. To select several vaccines hold down Ctrl on your keyboard.
Immunization information systems enable better and more timely decision-making. Landscape Analysis Trends in vaccine availability and novel vaccine delivery technologies. Concerted efforts by researchers on alternative vaccine delivery routes have yielded a range of novel delivery devices with potential to enhance immunogenicity and stability.
The use of information systems to collect store analyse and disseminate any relevant information. In this S pecial Focus experts in the field describe recent innovations in the design evaluation and use of novel vaccine delivery devices and systems. Contact the distributor 3.
Irache1 1 Adjuvant Unit Department of Pharmaceutical Technology and Microbiology University of Navarra 31080 Pamplona Spain. PLGA drug delivery systems have been approved by the FDA for the delivery of small-molecule drugs but not for the delivery of nucleic acids 147. Centre for Research and Development CHRD Maharashtra Association of Anthropological Sciences MAAS 18 July 2014 3 Determinants of vaccine effectiveness Efficacious vaccines Vaccine delivery systems Community awareness and.
January 22 2009 ii. Vaccine effectiveness Research framework Preliminary findings 18 July 2014 2 Research partner. Tretiakova and Elena L.
Contact the Department of Health Tip. Liposomes as Adjuvants and Vaccine Delivery Systems articleTretiakova2022LiposomesAA titleLiposomes as Adjuvants and Vaccine Delivery Systems authorDaria S. An overview of mRNA delivery systems and the lipid nanoparticle delivery systems used in the current SARS-CoV-2 vaccine clinical trials are presented and an analysis of the determinants of the performance of lipid nanoparticles in mRNA vaccines is analyzed.
Disadvantages of these vaccines are the need for an efficient delivery system low immune responses compared with live vaccines and the possibility of toxicity due to repeated injection doses. Vodovozova journalBiochemistry Moscow Supplement. The report searches all vaccines unless specified.
Vaccine strategies have been effective at stimulating specific immunity in the laboratory when injected by IP or IM methods more work is needed to develop better delivery systems and to overcome potential regulatory concerns. Delivery of antigens from oil-based adjuvants such as Freunds adjuvant lead to a reduction in the number of doses of vaccine to be administered but due to toxicity concerns like inductions of granulomas at the injection site such adjuvants are not widely usedFDA approved adjuvants for human uses are aluminium hydroxide and aluminium. It has been proposed that delivery of vaccine antigens to these tissues ie intradermal delivery rather than to muscle or subcutaneous tissue could therefore induce superior protective immune.
Lipid nanoparticles are among the most widely investigated nonviral vectors for the in vivo delivery of nucleic acid vaccines Support for the use of LNPs in the systemic delivery of short interfering RNA siRNA was provided in 2018 with the Food and Drug Administration FDAs approval of Onpattro patisiran for treatment of polyneuropathy caused by. Multiple delivery systems are being explored both developmental and clinical phases and can open the door for practical development of nasal vaccine delivery systems. At neutral pH PLGA does not have the positive.
RHsp60 liposome encapsulated rHsp60. The intranasal vaccine delivery system induces both mucosal and systemic immune response which avoids entry of pathogen in all mucosal routes. Supply systems support efficient and effective vaccine delivery.

Covid 19 Vaccine Frequently Asked Questions City Of Hamilton Ontario Canada

Virosome An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Pushing Boundaries To Deliver Covid 19 Vaccine Across The Globe
Covid 19 Vaccination Toolkit For Health Professionals
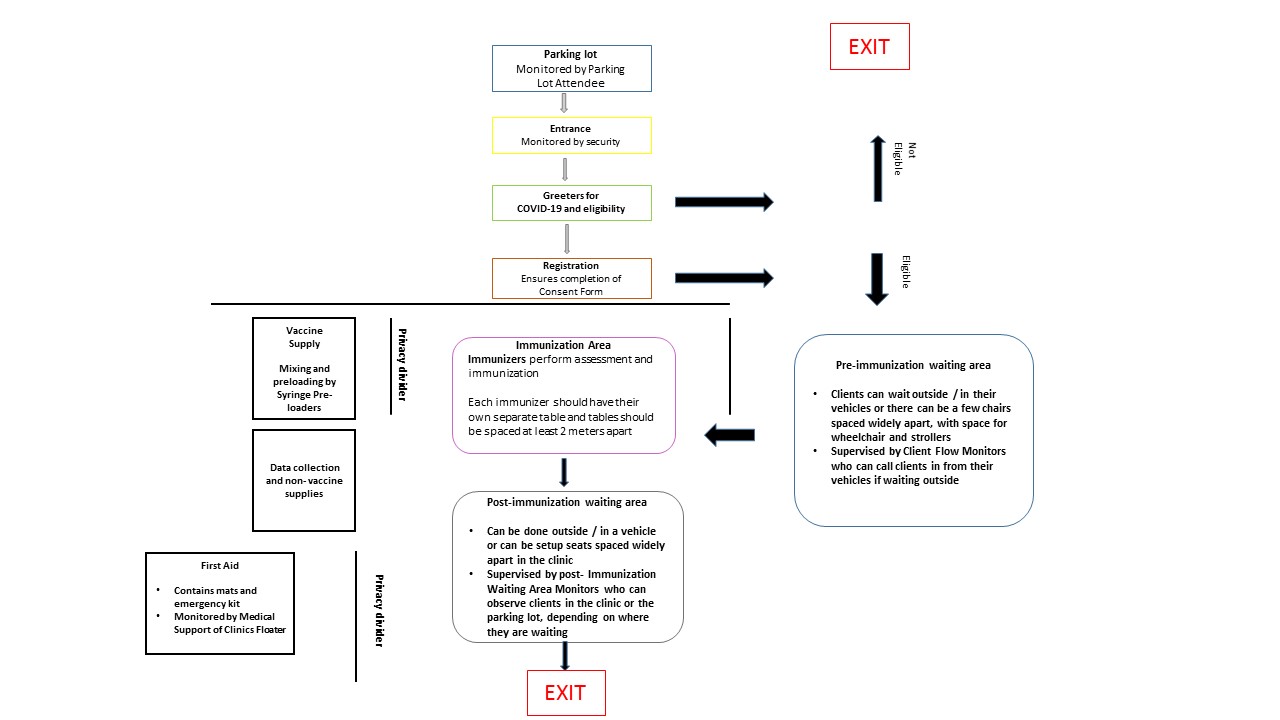
Covid 19 Vaccines Planning Guidance For Immunization Clinics Canada Ca

Controlling Timing And Location In Vaccines Sciencedirect

Essential Programme On Immunization

Optimization Of Lipid Nanoparticles For Intramuscular Administration Of Mrna Vaccines Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
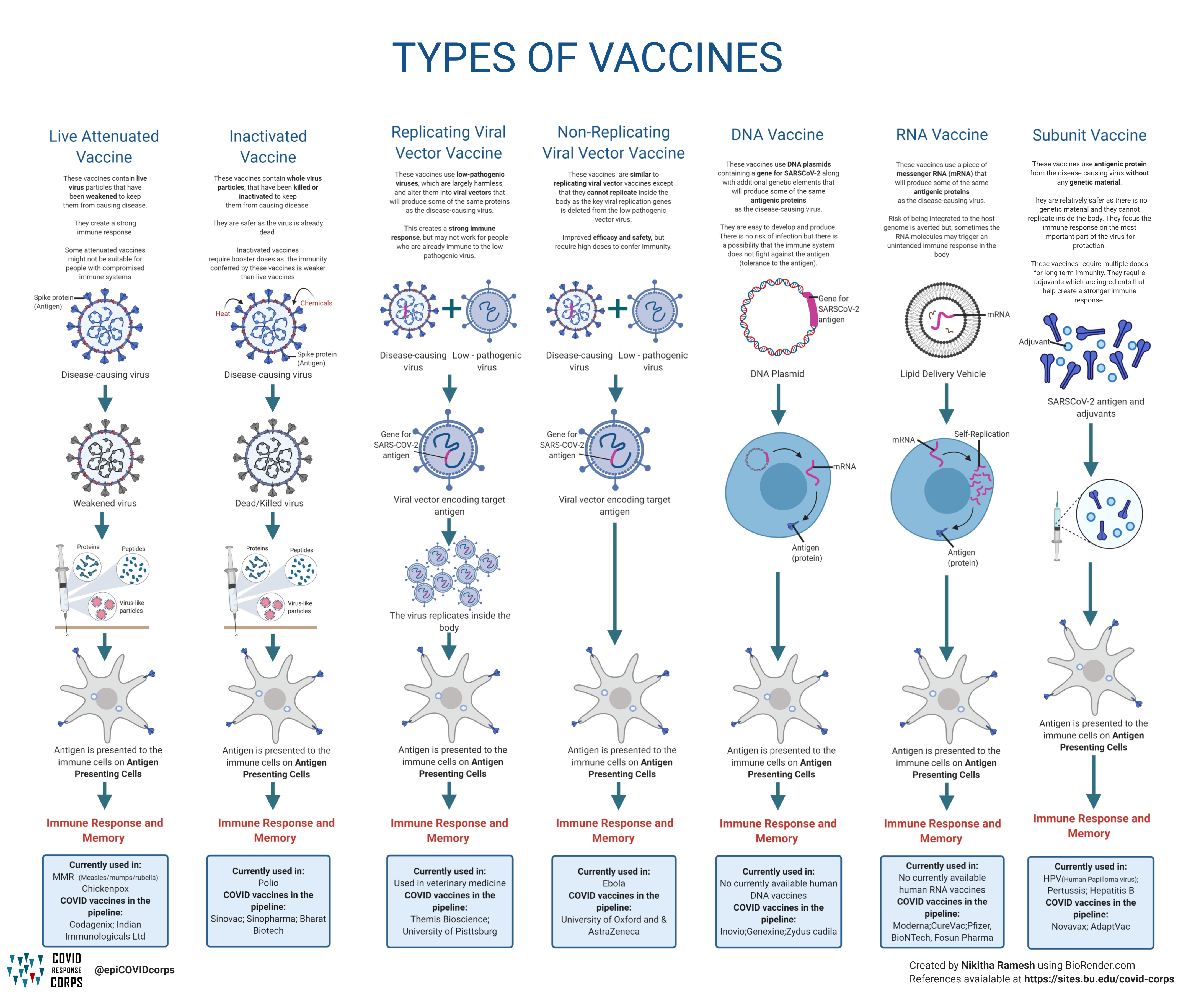
Types Of Vaccines Infographics Epidemiology Covid 19 Response Corps
How Are States Prioritizing Who Will Get The Covid 19 Vaccine First Kff

Africa Without Vaccines Inequity Sets The World On Course For A Great Divide Institute For Global Change
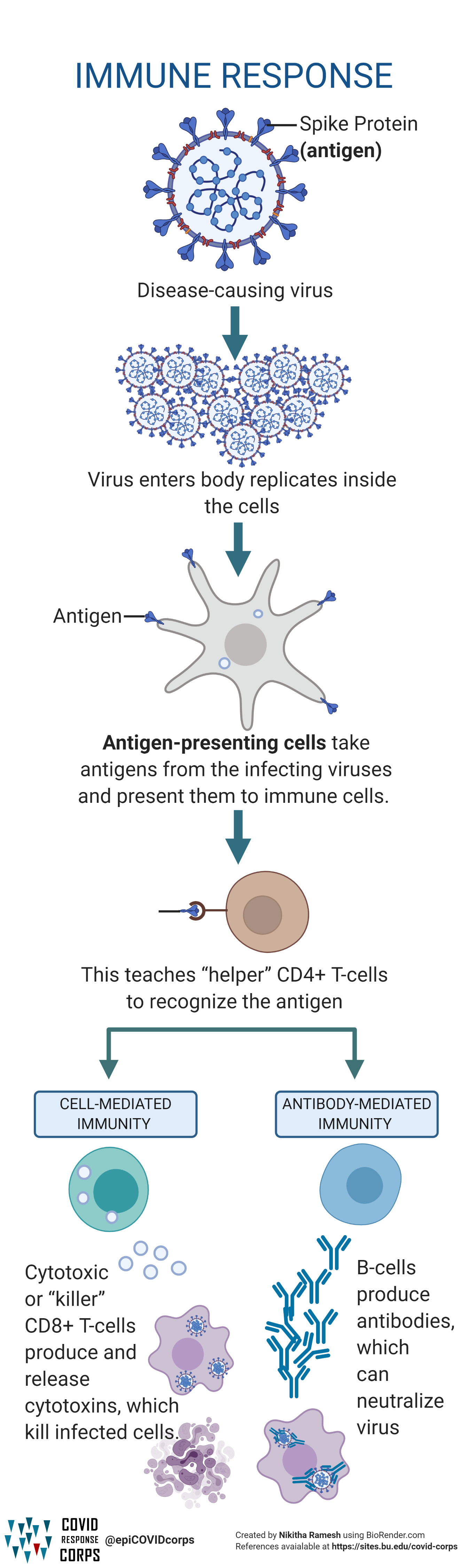
Types Of Vaccines Infographics Epidemiology Covid 19 Response Corps

Current And Future Nanoparticle Vaccines For Covid 19 Ebiomedicine
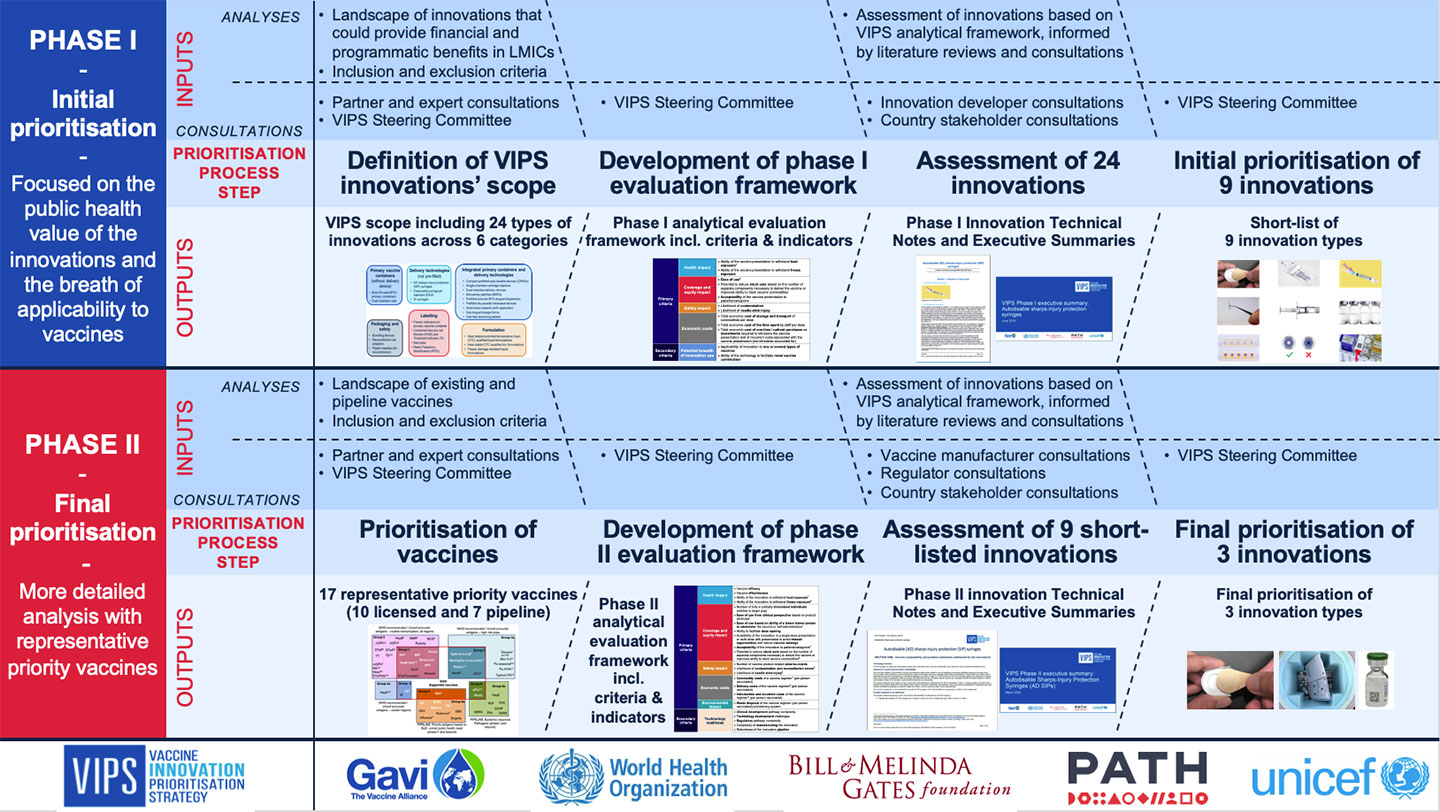
The Vaccine Innovation Prioritisation Strategy

Optimising Health And Economic Impacts Of Covid 19 Vaccine Prioritisation Strategies In The Who European Region A Mathematical Modelling Study The Lancet Regional Health Europe

Covid 19 Vaccine Frequently Asked Questions City Of Hamilton Ontario Canada